The International Phonetic Alphabet
Valencia, 21/04/2015, G.B.
Uno de los principales obstáculos que tenemos los estudiantes de inglés es
conseguir una buena pronunciación. Y una buena pronunciación es necesaria para hacernos entender adecuadamente. Solo con mucho esfuerzo, estudio y mucha más práctica, podemos lograr tener una pronunciación adecuada, aunque no sea perfecta.
Pronunciar correctamente nos evita situaciones delicadas y muy engorrosas, ya que el cambio de pronunciación de una sola vocal -y el inglés tiene muchos sonidos vocálicos- cambia radicalmente el significado de una palabra, como por ejemplo:
| sit /sit/ | shit /ʃit/ |
| cut /kat/ | cat /kӕt/ |
Para conseguirlo, además de escuchar todo el inglés que podamos (listenings) -ya sea British English, American English o cualquier otra variante nacional o regional- es importante conocer los símbolos fonéticos, cómo se representan gráficamente y cómo suenan, así como fijarnos en ellos cuando busquemos cualquier palabra nueva (o ya conocida, de paso) en el diccionario. Un buen diccionario incluye la transcripción de la palabra en el Alfabeto Fonético Internacional. Algunos ejemplos más:
| phonetic /fəˈnetik/ | alphabet /ˈӕlfəbit/ | international /intəˈnӕʃənl/ |
Un artículo que os recomiendo al respecto que he encontrado es este:
The sounds of English and the International Phonetic Alphabet. En él, podéis ver representados y escuchar los signos fonéticos del idioma inglés. El artículo en sí está más enfocado al
American English, más que nada en cuanto a la pronunciación, pero cuando esta es muy distinta al
British English, lo especifica y diferencia. Os recomiendo su lectura y/o estudio, a ser posible…
Otros recursos interesantes, entre otros muchos más:
Phonemic chart (British Council)
Phonetics (Cambridge Dictionaries Online)
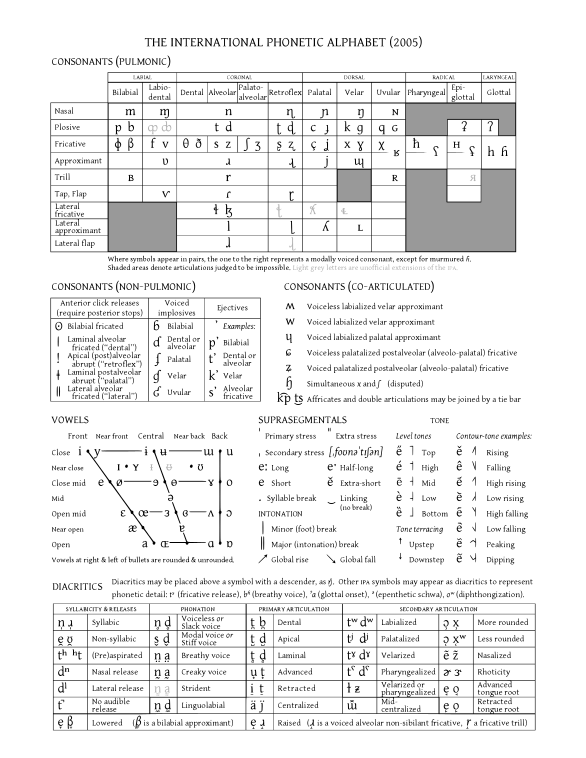 |
| Fuente: Wikipedia |
 Así, un compilador (compiler) es un programa informático o conjunto de programas que transforma código fuente escrito en un lenguaje de programación en otro lenguaje de ordenador habitualmente binario. El objetivo es convertir el código fuente en un programa ejecutable (executable).
Así, un compilador (compiler) es un programa informático o conjunto de programas que transforma código fuente escrito en un lenguaje de programación en otro lenguaje de ordenador habitualmente binario. El objetivo es convertir el código fuente en un programa ejecutable (executable). Así, un compilador (compiler) es un programa informático o conjunto de programas que transforma código fuente escrito en un lenguaje de programación en otro lenguaje de ordenador habitualmente binario. El objetivo es convertir el código fuente en un programa ejecutable (executable).
Así, un compilador (compiler) es un programa informático o conjunto de programas que transforma código fuente escrito en un lenguaje de programación en otro lenguaje de ordenador habitualmente binario. El objetivo es convertir el código fuente en un programa ejecutable (executable).